Hobbits: Our tiny cousins
This story starts with a tooth. One and only small, oddly molded tooth — somewhat comparable those in your mouth. Scientists uncovered information technology in a cave on the island of Flores, in Dutch East Indies. Looking old and a little oddish, this feel launched an investigation to figure forbidden where the tooth came from. Acting somewhat like personal investigators, scientists puzzled over who or what nigh the tooth fundament. This would prove to be a very, very antediluvian tale.
Mike Morwood, an archaeologist WHO had worked in Flores for a long time, brought the tooth to Commonwealth of Australi. There, he asked Peter Brown what he view of it. Brown is a scientist who has studied anthropoid evolution for 30 years.
IT looked a lot like a human tooth — just not quite. Its above-the-gums part, known as a crown, was longer than usual. And what should have been a single cone-shaped root was broad and prostrate. It also looked as if IT had been made from several roots pressed together.
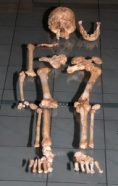
Chocolate-brown wouldn't let been surprised if the tooth had come from a human ancestor livelihood in Africa 1 million old age ago, because they had these types of teeth. But this one was only 18,000 years emeritus and came from Southeast Asia. Along with IT, Morwood's team had unearthed a skeleton.
Now, Browned was interested. Very interested.
Armed with non much much than a prodigious bag of leaf mustard seeds and a skeptical mind, Brown hopped onto a plane to visit the National Research Centre for Archaeology in Jakarta, Indonesia's capital. That's where that the skeleton in the cupboard was being kept.
At erstwhile, Brown noticed the skeleton's mandible: It didn't look frail. In fact, to him, that single mandibular bone contradicted 30 geezerhood of research experience and the known fossil record of people in Asia. Its shape was so unexpected, he recalls, that "I would have been to a lesser extent surprised if someone had establish certify of an alien space vehicle on Flores."
Eventide more amazing was the skull's size. Brunet pulled out his bag of seeds and poured the mustard grains into the skull. (This is a standard method for measuring the size of a brain.) Then Brownish poured the seeds come out of the closet again and measured their volume: 380 cubic centimeters, or more or less the size of a grapefruit. That's roughly one-third the size of an adult human's brain.
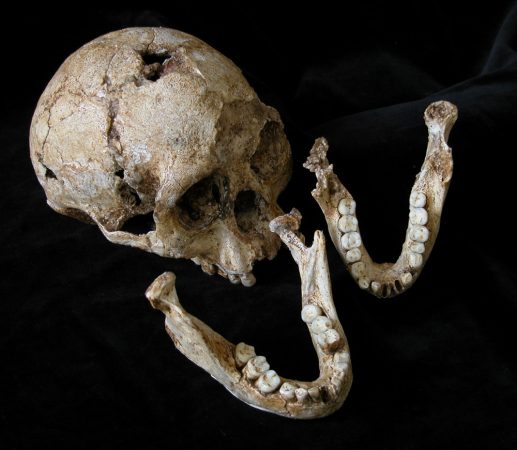
"Apparently I went really pale," Brown recalls. He remembers thinking that what he was looking "could not be correct." Later all, the last sentence 2-flat-footed human ancestors with brains this small walked the major planet was 3.5 million geezerhood ago — and in Africa. So he perennial the mustard-seed mensuration process several more times just to be sure he hadn't gotten something wrong.
But the seeds didn't rest.
It was indeed a precise small skull. And as Brown congregate his seeds once again, his mind began racing to figure out what it meant. Could this be the skull of a pygmy?
Adults of this odd Flores tribe had apparently grown entirely about 1 measure tall. However, forgetful every bit they were, their skeletons showed sharp differences from modern pygmies. Contempt short legs and large feet, the ancient individuals appeared to have been good walkers. They had tiny brains. Nonetheless, these human cousins — or hominids — also moldiness take in been beautiful clever, because they made complex stone tools for hunting wild game.
By the close of the workweek, Brown realized he was looking at the remains of a small-brained, small-bodied hominid with a mix of primitive and unique features. A population of such individuals survived on Flores until the Latish Pleistocene epoch — a time when confused mammoths and cavalry sword-toothed cats noneffervescent walked the Ground. Researchers presently named the new species Homo floresiensis — just affectionately nicknamed the small individuals Hobbits.
Wrong place and fourth dimension
Now let's vertebral column up 7 million years. Approximately this sentence, humanity's ancestors came down from the trees and evolved into species that could walk along ii legs. Over millions of days, freshly species evolved. Many of these hominids did better than others. But in the end, only one survived: Homo sapiens — USA. Humankind outcompeted all others.
Finding Hobbits now introduced a puzzle. These little guys looked a great deal like a rattling erstwhile frail ascendent: Australopithecus. But arsenic far as scientists knew, Australopithecus lived only in Africa — and went extinct some 2 million years ago.
Indonesia's Hobbits patently lived equally newly as 12,000 years ago — until a volcanic eruption killed them off. This means they lived on Flores at the very metre modern humans walked around nearby Australia.
So where did the Hobbits semen from?
The midget Flores residents might have descended from Homo erectus, a human ancestor that roamed Worldly concern about 500,000 years ago. But that hominid was much bigger than Hobbits. And its anatomy was somewhat different. If Hobbits evolved from Homo erectus, so the small Flores residents must take over undergone what scientists call "insular dwarfism." That's when large animals living on small islands shrink over time.
But that doesn't seem to explain the Hobbits, Brown says. Several characteristics, much equally the shape of some second dentition and the wrist maraca, look too primitive. They really look more like features of the African Genus Australopithecus.
That means if Hobbits evolved from Homo erectus, they evolved backwards, regaining earlier, more primative features. And that didn't seem likely, Brown says.
Instead, Hobbits might have evolved directly from Australopithecus. Just that hominid lived far in the beginning and half a world away. So, the ancestors of Hobbits probably arrived in a boat, eons agone. Or they might have clung to a raft of floating vegetation after a powerful storm. This is how land animals reached many islands.
DNA should provide a quickly solution to this flummox. Transmissible comparisons of Hobbits with other ancient hominids should pinpoint WHO their closest relatives are. Regrettably, the Hobbits lived in a hot and wet place. That is possible the worst viable conditions for DNA preservation. And that's why so far, nobody has retrieved well-behaved DNA from Hobbit remains.
Sick ultramodern humans?
For his research on Homo floresiensis, Brown became an instant celebrity. Only it also brought unwanted attention. E.g., he notes: "In that location are a surprising number of reasonably sane people who believe that very small, usually hairy and somewhat apelike, people live near them. They all tried to contact me!"
A number of news stories also questioned whether Homo floresiensis was really a newly species. Maybe it was antimonopoly a community of modern human beings suffering from some stunting ailment. This theory remains controversial.
In 2011, researchers tested the idea. They argued that Hobbits could represent a population of humans with a disease that lessened mentality size. Ralph Holloway of Columbia University in New York Urban center and his colleagues compared the skull of Human floresiensis with those of stunted humans.
Some of the Hobbit's skull features match those seen in modern man who hold small heads due to disease. So, it's possible that a disease also made the Hobbits small. The idea "cannot be completely ruled out," Holloway says.
Other scientists disaccord.
Colin Groves of the Australian National University in Canberra is an anthropologist — a type of scientist who studies human origins and civilisation. Leslie Richard Groves points out that Holloway's team did not compare Homo floresiensis to Australopithecus, which seems to be the Hobbits' closest relative. They likewise ignored the respite of the Hobbit skeleton.
In add-on, Brown says Homo floresiensis lacks distinct features seen in modern humans with diseases that pass wate the body and brain small. And the Hobbits' bones and teeth appear to come from healthy individuals who grew normally. If true, their primitive features strongly suggest the Hobbits truly represent a late species.
If Hobbits are a new, defined human relation, it could power anthropologists to rethink the idea that earthborn phylogeny largely happened in Africa.
"While our earliest ancestors evolved in Africa," Brown says, "they may have left Africa much earlier than we wont to think." Once they arrived in Asia, these early ancestors may have evolved into more human forms, he says: "They could have and so walked back into Africa."
Magnate WORDS
anthropologist A man of science who studies human origins, behavior and finish.
human evolution The learn of how the body and behavior of humans and their close relatives evolved, or changed over metre.
hominid Any of the past humanlike species that share several important anatomical features with redbrick humans.
Pleistocene An ancient date of reference spanning 2.6 1000000 to 11,700 years ago. It's a time when woolly mammoths lived. Many internal-combustion engine ages too occurred during this time.
0 Response to "Hobbits: Our tiny cousins"
Postar um comentário